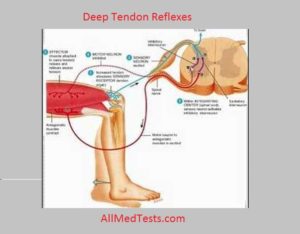
Deep Tendon Reflex:
If a tendon of a lightly stretched muscle is struck with a single sharp blow with a soft rubber/ clinical hammar, the muscle contracts briefly and briskly. This is the monosynaptic stretch reflex. It is test of the integrity of the afferent and efferent pathways, and of the excitability of anterior horn cells in the spinal segment of the stretched muscle.
Make sure that subject is calm and comfortable. He should be completely relaxed with diverted attention.
Grading of Reflexes:
- Grade 0 = Absent
- Grade 1 = Present ( As a normal ankle jerk).
- Grade 2 = Brisk ( As a normal knee jerk).
- Grade 3 = Very Brisk
- Grade 4 = Clonus
Clonus is sign of increased reflex activity characterized by repetitive muscular contraction produced by stretch.
Abnormal Tendon Reflexes:
- Reflex diminishes or absent:
During sleep
Lower motor neuron lesion. - Reflex exaggerates:
Anxiety or nervousness.
Upper motor neuron lesion.
Thyrotoxicosis.
Deep (Tendon) Reflexes:
- Knee jerk.
- Ankle Jerk.
- Triceps Jerk.
- Biceps Jerk.
- Supinator Jerk.
- Jaw Jerk.
These are elicited as follow:
1. Knee jerk:
This reflex can be elicited in lying or sitting positon.
Lying Position:
Ask the subject to lie supine. Ask the subject to raise both the knee by flexing knee and hip joint. Pass your hands under the knee to be tested and place on the other knee. Now strike the pateller tendon midway between its origin and insertion.
Sitting Posture:
Subject is asked to sit on the bed with leg hanging freely over the other knee or the edge of the bed. Now strike the tendon with pateller hammer.
Thigh region of the patient should be uncovered. Reflex shows a brief contraction of quadriceps femoris muscle resulting in extension of the knee.
Jendrassik’s manoeuvre:
If there is no response ask the subject to hook the fingers of two hands together and then to pull them against one another as hard as possible or to make a clench fist with ispilateral hand, this is called Jendrassik’s manoeuvre or Reinforcement.
This would divert his/her attention and increase generalized muscle tone or anterior horn cell excitability. Spinal segments involved in the reflex are second, third and fourth lumber nerves.
2. Ankle Jerk:
It is elicited in supine posture. Place the lower limb of the subject in everted slightly flexed position, then with one hand, slightly dorsiflex the foot so as to stretch it (achille’s tendon). Strike the tendon of Gastrocnemius muscle (calf muscle) with the other hand. Reflex is shown as sharp contraction of calf muscle leading to planter flexing of ankle joint. If there is no response Jendrassik’s Manoeuvre may be performed. Spinal segments involved in the reflex are S1 and S2.
3. Triceps Jerk Reflex:
Ask the subject to lie supine. Flex the elbow and allow the forearm to rest across the subject’s chest. Take the triceps tendon just above the olecronon with narrow end of patellar hammer. The triceps contraction might be leading to extension at elbow. Spinal segments involved in the reflex are C6 and C7.
Other method to elicit the reflex is that support the forearm of the subject with your left hand in semiflexed position. Strike the triceps tendon above olecronon with right hand.
4. Biceps Jerk Reflex:
The elbow is flexed to a right and the forearm placed in a semi pronated position. Then you place your thumb or index finger on the biceps tendon and strike it with pointed end of platellar hammer. The biceps contraction might be leading to flexsion at elbow joint. Cervical 5 and 6 spinal segments are involved in this reflex.
5. Supinator Jerk Reflex:
The elbow is flexed to a right angle and forearm placed in semipronated position. Tap the supintor (brachioradialis) tendon upon the styloid processes of radium. Supinator muscle contracts leading to supination of elbow. Cervical 5 and 6 spinal segments are involved in this reflex.
6. Jaw Jerk:
Ask the patient to open his mouth a bit but not too widely. Place one finger of left hand firmly on his chin and then tap it suddenly with finger of right hand. Masseter muscle contracts resulting in closure of the jaw. Trigeminal nerve (fifth cranial nerve) is involved in this reflex.
Precautions for Tendon Reflexes:
- There should be no joint disease of the subject.
- Explain the procedure to the subject before eliciting the reflex and the ask for consent.
- Subject should be relaxed and the part of the body to be tested should be fully exposed.
- The examiner should concentrate on the movements of muscles and not the joints.


I have a brisk jerk in my chin my speech is slurred nstuddering bad headache dizzy blew my nose ndark blood came out
consult an ENT specialist.