Apparatus:
Patellar hammer and Examination couch, subject, cotton wool, torch, tongue depressor, probe.
Clinical hammer/patellar hammer consists of a long metallic handle, at one end of it is a triangular rubber piece is attached. The rubber piece has two ends, one pointed in other broad. This rubber piece is used to give a sharp blow but light preferable by free fall of hammer from a suitable height to a tender, in order to cause sudden scratching of the muscle.
During eliciting the reflex, make sure that subject should be comfortable and relax. Skin overlying the muscle tested should be recovered to see the contraction (response) of the muscle.
Principle:
Reflex action is involuntary response of effectors to an appropriate stimulus without the intervention of will. The examples of the superficial reflexes are:
- Corneal Reflex.
- Conjunctival Reflex.
- Pupillary Reflex.
- Pharyngeal Reflex.
- Scapular Reflex.
- Abdominal Reflex.
- Cremasteric Reflex.
- Planter Reflex.
- Anal Reflex.
Examination:
Superficial Reflexes:
They are polysynaptic. Centre are various integrated supraspinal levels. These reflexes are of significance in unilateral lesions when healthy side is taken as standard for comparison purposes. These are depressed in upper motor neuron lesion as compared to deep reflexes which are exaggerated.
1. Corneal Reflexes:
The subject is asked to look at seiling and blow a puff of air into the eye. The subject will close the eye and reflex will be positive. The same procedure is repeated on the other eye.
2. Conjunctival Reflex:
A wisp of cotton is twisted to make a fine thread. The subject is asked to look upward. The lateral part of the sclera is touched with the cotton. The person will blink his eye and the conjunctival reflex is positive. The same procedure is repeated on the other eye.
3. Pupillary Light Reflex:
Ask the subject to look at a certain object. The light is thrown into his eye by a torch from the side. The constriction of the pupil shows that the reflex is positive. The constriction of the pupil of the opposite eye is known in consensual light reflex. The same procedure is repeated on the other eye.
4. Pharyngeal Reflex:
This is also called palatal reflex.
Ask the subject to close his eye and open the mouth. The tongue of the subject is depressed by a tongue depressor. The posterior wall of the pharynx is touched with a probe and the contraction of the pillars of the tonsillar fossi are noted.
5. Scapular Reflex:
The skin in the interscapular region is scratched and contraction of the scapular muscle is noted. The nerve supply of this reflex is 5th cervical to 1st thoracic nerves.
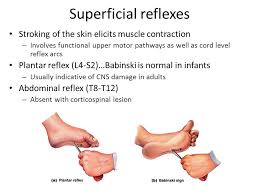
6. Abdominal Reflexes:
Stroke the abdominal wall gently with key or wooden stick parallel to coastal margins and inguinal ligament when subject is laying in supine with uncovered abdomen. Normally this leads to contraction of underlying muscles . Positive reflex is shown by the movement of umbilicus and contraction of abdominal muscles. It is usually difficult to obtain this reflex in anxious persons, elderly, obese and multipara women.
Level of spinal cord involved in the reflex is seventh thoracic to twelfth thoracic.
7. Cremasteric Reflex:
Stroke the skin at upper and inner path of thigh, testicles are drawn upward or retracted upward because of contraction of cremasteric muscle. Spinal segments involved in this reflex are first and second lumber nerves.
8. Planter Reflex:
subject is asked to lay on the bed or cough in supine position. Gently scretch the outer edge of the foot with blunt object such as key etc from the heel towards little toe and then medially across the metatarsal. Flexion of the four outer toes takes places with increased strength of stimulus all the toes are planter flexed adducted ankle become dorsiflexed and inverted (babinski’s sign negative). This is called flexor planter response. With still stronger stimuli withdrawl of the limb occurs.
In case of upper motor neuron lesion planter response becomes extensor planter response. It is called as babinski’s sign.
It is also positive in children below one year of age. It is because myelination of corticospinal pathway gets completed in six to twelfth months.
In the extensor planter response, dorsiflexion (extension) of great toe and spreading out (fanning) and extension of other toes. Level of spinal cord involved in the reflex is L5 and S1.
It is also positive in sleep.
9. Anal Reflex:
Stroking or scratching the skin near anus leads to contraction of anal spincter. Spinal segments involved in the reflex are S3 and S2.


Leave a Reply