Third, Fourth & sixth Nerve Test:
They control ocular movements so considered together. They are mixed nerves. They bring sensations from proprioceptors in the eye muscles.
Fibers of these nerves take origin from a series of nuclei which begin in the floor of sylvian aqueduct and extending up to the fourth ventricle. Abducent nerve innervates the lateral (external) rectus muscle and trochlear innervates the superior oblique muscle. All other extra ocular muscles, the spincter pupillae muscles of accomodation and the levator palpebrae superioris are supplied by oculomoter nerve.
Role of extraocular muscles in movement of eye ball can be learn here.
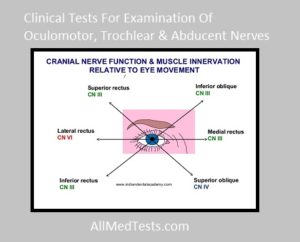
How to Test:
Look For Ptosis:
Drooping of upper eyelid.
Look for squint:
Abnormality of ocular movement in which axis do not meet at the point of fixation.
Nystagmus:
Involuntary rhythmic to and fro movement of eye ball.
Test for Ocular Movements:
Ask the subject to follow the movement of examiners finger with his eye in superior, medial, inferior, lateral and oblique directions. Stabilize the subject chin to prevent head movement. The examiner should observe that the movement of eye ball are smooth. If the full movement occurs, it is indicated that the muscles strength and nerve function is intact.
Examination of pupil:
Examine the size and shape of the pupil in both the eyes.
Check for pupillary reflexes i.e:
- Light Reflex (direct as well as indirect/consensual)
- Accommodation Reflex.
1. Light Reflex:
Direct Light Reflex:
It is done with the help of pen torch in dim light room. Each eye is examined separately. Ask the subject to see at a distant object. Through a bright light with the help of torch by bringing it from lateral side of the eye. Immediately observe the size of the pupil. Normally it should constrict.
Indirect/Consensual Light Reflex:
Project the light in one eye only and observe the response in other eye. In this reflex other eye also shows contraction of pupil. To prevent entry of light in other eye the hand is placed at the nose in between the eyes.
2. Accommodation Reflex:
When a person is asked to see a near object from distinct object, certain changes are taking place to see the near object clearly. These are:
- Increase in the power of the lens by contraction of ciliary muscles.
- Constriction of pupil which cause to decrease spherical and chromatic aberrations, intensity of light entering into the eye and to increase the depth of focus.
- Convergence of visual axis due to contraction of medial rectus muscle.


Leave a Reply